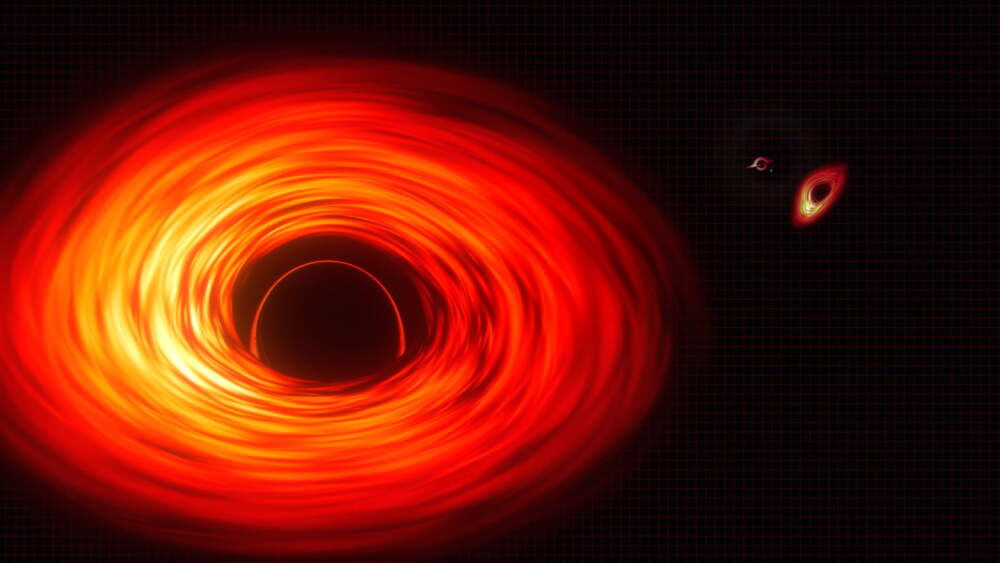
Astronomers have identified what may be the most massive black hole ever recorded—an astronomical giant with a mass equal to 36 billion Suns. This ultramassive black hole resides roughly 5 billion light-years away, buried in the heart of a galaxy nicknamed the Cosmic Horseshoe.
How Scientists Found It
Researchers used a combination of gravitational lensing and stellar kinematics to detect and measure the black hole. Gravitational lensing occurs when an extremely massive object bends and magnifies light from more distant galaxies, creating striking arcs or rings in the sky. The stars in the host galaxy were also found to be moving at extremely high speeds—close to 400 kilometers per second—pointing to the presence of an unimaginably dense central object.
Why This Discovery Stands Out
Many giant black holes are identified indirectly, and their estimated masses often come with large uncertainties. This case is different because scientists employed two independent methods that both point to the same colossal size, giving the measurement far greater reliability.
Context Among the Universe’s Giants
While this black hole ranks among the heaviest ever measured, other candidates like TON 618 may be even larger—potentially around 66 billion solar masses—but those estimates are far less certain due to their extreme distance.
A Window Into Cosmic History
The Cosmic Horseshoe galaxy is thought to be a fossil galaxy, meaning it likely formed from the merger of several large galaxies long ago. In such events, their central black holes would also merge, possibly explaining how a single object could grow to such a massive scale. Discoveries like this challenge current models of how black holes form and evolve, especially so soon after the Big Bang.
What Comes Next
Astronomers plan to apply the same measurement techniques to other galaxies to uncover more hidden ultramassive black holes. Upcoming space missions, equipped with advanced telescopes, could soon reveal a population of these cosmic monsters—reshaping our understanding of the largest objects in the known universe.












Leave a Reply