The American Heart Association (AHA) has unveiled updated guidelines on hypertension, revealing that nearly 50% of U.S. adults now meet the criteria for high blood pressure. This significant rise underscores the urgency for early detection and proactive management to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and cognitive decline.
Key Highlights of the 2025 AHA Hypertension Guidelines
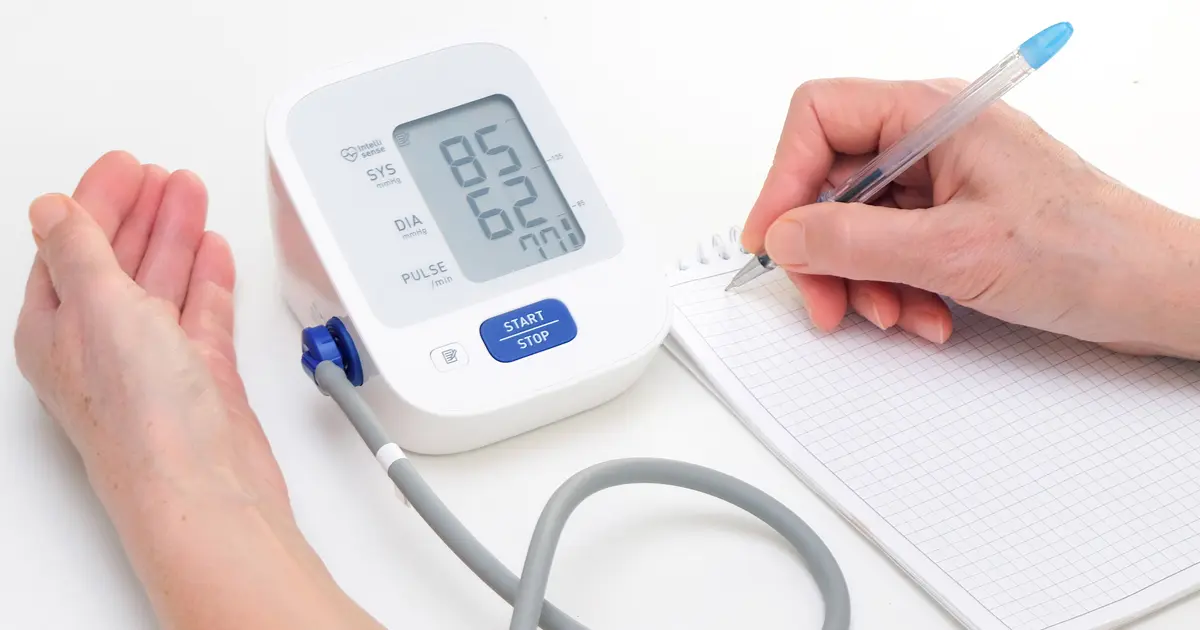
1. Updated Blood Pressure Classification
- Normal: Less than 120/80 mm Hg
- Elevated: 120–129/<80 mm Hg
- Stage 1 Hypertension: 130–139/80–89 mm Hg
- Stage 2 Hypertension: ≥140/≥90 mm Hg
Despite unchanged categories, the guidelines emphasize that nearly half of U.S. adults now fall into the elevated or hypertensive ranges, highlighting the need for increased awareness and intervention.
2. Early Intervention with Risk Assessment
A notable addition is a risk calculator designed to assess long-term cardiovascular and brain health by integrating data on blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney function, and metabolic health. This tool helps clinicians make informed decisions about initiating treatment, even for individuals with stage 1 hypertension, particularly those with additional risk factors.
3. Lifestyle Modifications as First-Line Therapy
The guidelines advocate lifestyle changes as the cornerstone of hypertension management:
- Diet: Adopt the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
- Sodium Intake: Limit sodium to less than 2,300 mg daily, ideally 1,500 mg.
- Alcohol Consumption: Minimizing or avoiding alcohol is recommended for optimal blood pressure control.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise.
- Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing practices like meditation or yoga.
4. Medication Considerations
For individuals whose blood pressure remains elevated despite lifestyle changes, medication may be necessary. The guidelines suggest initiating therapy with two medications for stage 2 hypertension, while stage 1 hypertension may also require treatment in the presence of cardiovascular disease. Common options include ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics.
5. Hypertension Management During Pregnancy
Monitoring and managing blood pressure during pregnancy is critical to prevent complications such as preeclampsia. Treatment is recommended when blood pressure reaches 140/90 mm Hg or higher to reduce risks to both mother and child.
The AHA’s updated guidelines emphasize early detection and comprehensive management of high blood pressure. By adopting these recommendations, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of severe cardiovascular and neurological conditions.












Leave a Reply