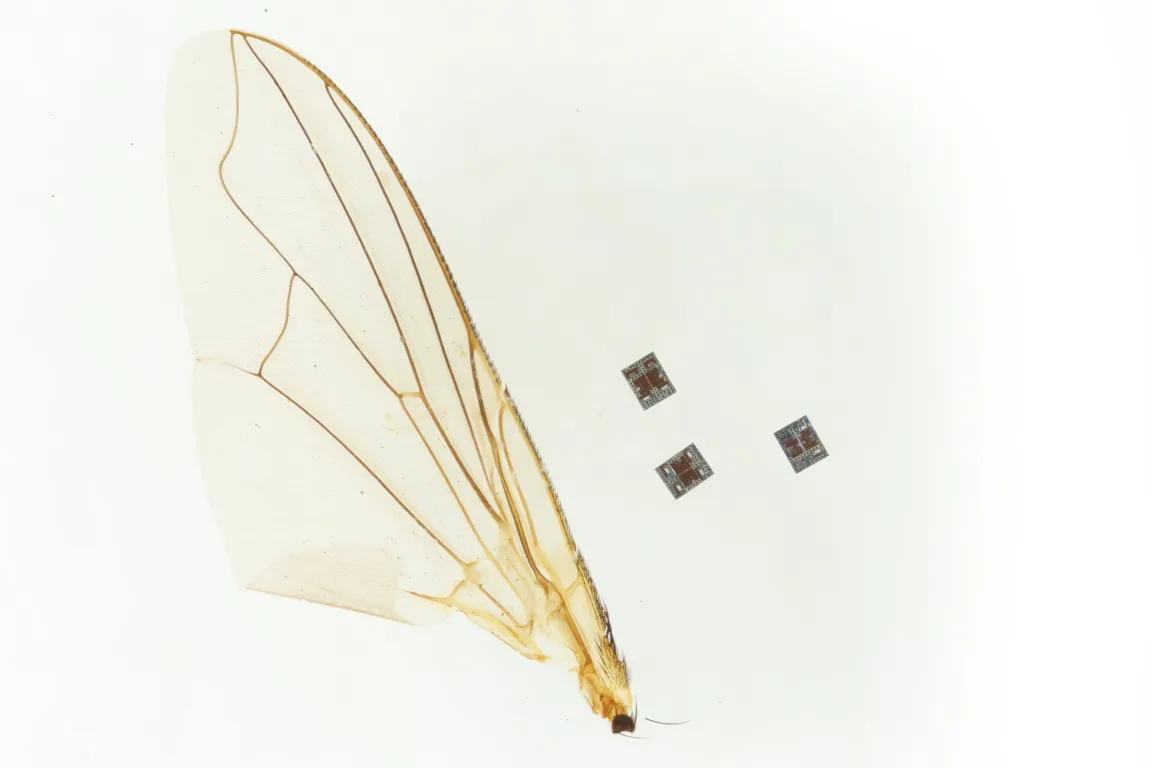
In a groundbreaking development, researchers have unveiled a robot small enough to travel through the human body, opening new frontiers in diagnostics, targeted therapy, and minimally invasive medicine. The tiny device, no larger than a human cell, promises to revolutionize how doctors treat diseases, monitor internal systems, and deliver precision treatments directly to affected areas.
Miniaturized Robotics Meets Medicine
The newly developed robot is designed using micro-scale engineering and advanced materials, allowing it to move through blood vessels, digestive tracts, and other narrow bodily pathways without causing damage. Its compact size enables it to reach areas of the body that were previously inaccessible using traditional medical tools.
Equipped with sensors, micro-cameras, and programmable navigation systems, the robot can map internal structures, detect anomalies, and deliver targeted therapies. Researchers emphasize that such capabilities could dramatically reduce the need for invasive surgical procedures and improve treatment outcomes for conditions ranging from cardiovascular disease to gastrointestinal disorders.
How It Works
The robot’s movement is controlled through a combination of magnetic fields, micro-actuators, and AI-driven guidance algorithms. Physicians can steer it remotely, monitor real-time data, and adjust its path or behavior as needed. Some prototypes also feature payload delivery systems, enabling the precise release of medication directly at the site of disease.
The device is biocompatible and designed to minimize immune system interference, ensuring safe passage through sensitive tissues. Early laboratory tests have demonstrated that the robot can navigate complex biological environments with a high degree of accuracy and stability.
Potential Applications
The implications of this technology are wide-ranging:
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Administering medication directly to affected tissues can improve effectiveness while reducing systemic side effects.
- Early Disease Detection: Tiny sensors and cameras allow for high-resolution imaging inside the body, potentially identifying tumors, blockages, or infections at an early stage.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Robots could perform micro-procedures that currently require invasive surgery, reducing recovery time and patient risk.
- Precision Diagnostics: Continuous monitoring of blood chemistry, pressure, and other biomarkers could become feasible with fleets of such microscopic robots.
Challenges and Next Steps
Despite its promise, the technology faces several hurdles before widespread clinical use. Researchers must ensure that the robot can be safely retrieved or dissolved after completing its mission, that it operates reliably in diverse biological conditions, and that long-term effects on human tissues are minimal. Regulatory approval and rigorous clinical trials will be necessary before adoption in hospitals and clinics.
A Glimpse Into the Future
Experts believe that the successful integration of microscopic robots into medicine could transform healthcare, making treatments more personalized, precise, and less invasive. Over time, swarms of such devices could work in concert to monitor multiple aspects of patient health, creating a new paradigm in preventive medicine and real-time diagnostics.
One of the lead scientists remarked, “This is not just a step forward in robotics—it’s a leap toward a future where medicine can reach places inside the human body that were once considered unreachable.”
As research continues, the medical community is closely watching the potential of these tiny robots to redefine treatment, diagnostics, and patient care across multiple disciplines.













Leave a Reply