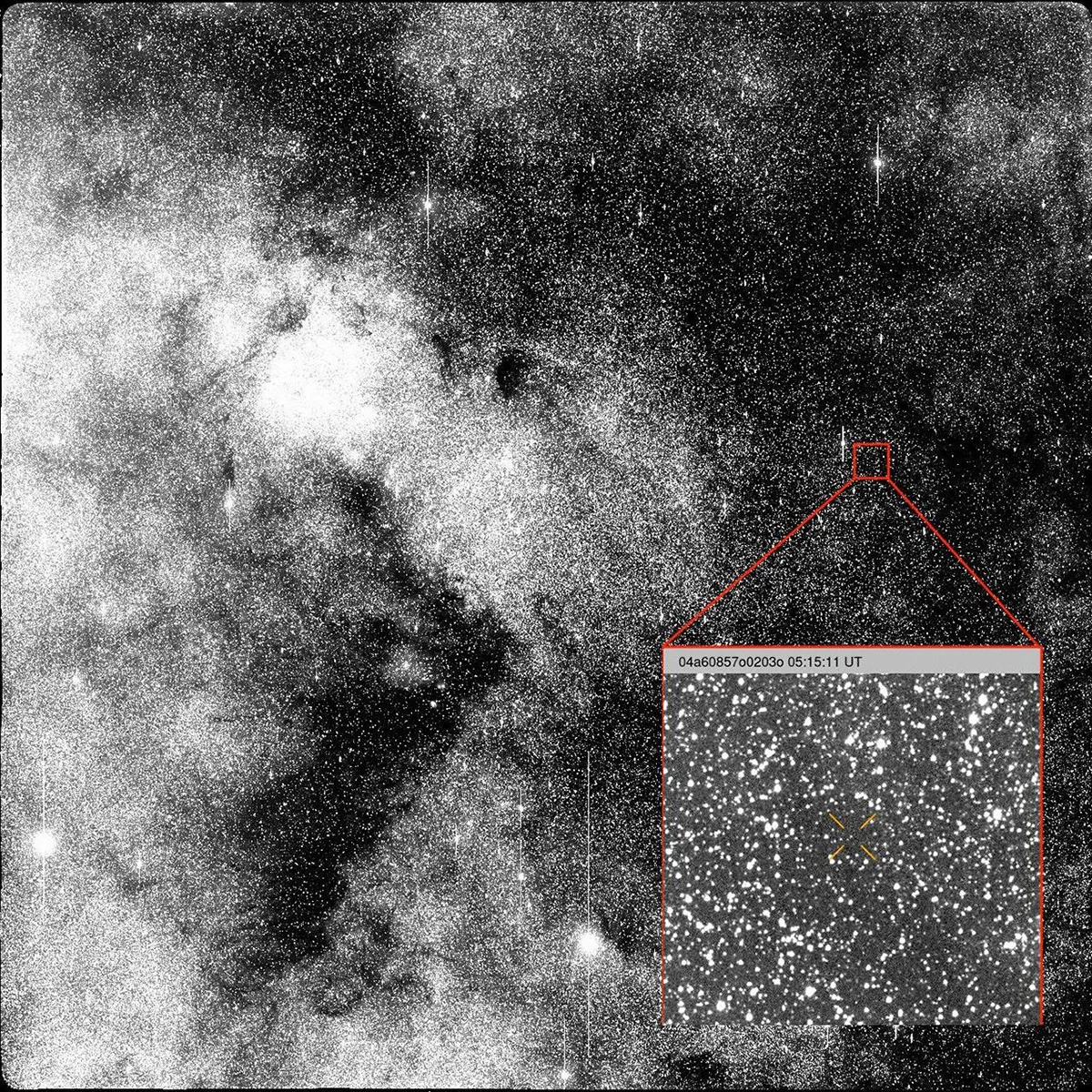
Astronomers are closely monitoring the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS after it recently displayed unexpected changes in its path, challenging predictions about its movement through the solar system. This rare visitor, only the third confirmed object from beyond our solar system, continues to intrigue scientists with both its trajectory and unusual physical behavior.
A Rare Visitor from Another Star System
Discovered in mid-2025, 3I/ATLAS follows a hyperbolic trajectory, meaning it is on a one-time journey through the solar system and will never return. Unlike typical solar system comets, which travel in elliptical orbits governed mainly by the Sun’s gravity, interstellar objects arrive at high speeds with trajectories shaped by complex forces, making their behavior more difficult to predict.
Recent observations revealed that the comet has slightly deviated from its expected course, likely due to outgassing — the process where volatile ices on its surface turn into gas as it warms near the Sun. These jets act like tiny thrusters, subtly altering the comet’s speed and direction. While outgassing is common among comets, it has made modeling 3I/ATLAS’s long-term path particularly challenging.
Unusual Physical Features
In addition to its erratic path, 3I/ATLAS exhibits unique features in its tail and surrounding cloud of gas and dust, known as the coma. Observers have reported an unusual “anti-tail” that appears to point toward the Sun, a phenomenon caused by the orientation of dust particles relative to Earth. The comet also shows wobbling jets of material, indicating a complex rotation pattern and highly active surface regions.
Scientists have detected significant amounts of water vapor and other gases being released, even at distances where such activity is unexpected for standard comets. This intense outgassing suggests a larger-than-normal active surface area, potentially reflecting its origin in a different star system with unique environmental conditions.
Scientific Importance
While 3I/ATLAS poses no threat to Earth, its visit provides an extraordinary opportunity to study material from another planetary system. Researchers are using it to better understand cometary behavior, outgassing effects, and the influence of non-gravitational forces on small celestial objects. Studying its chemical composition and physical characteristics could offer insights into the diversity of planetary systems beyond our own.
Observations and Collaboration
Global observatories are coordinating efforts to track 3I/ATLAS as it continues on its rapid exit from the solar system. The comet’s unpredictable nature makes continuous observation essential to refine scientific models and improve our understanding of how interstellar objects behave under the influence of the Sun.
Astronomers hope that the data collected from 3I/ATLAS will inform future studies of similar visitors and deepen our knowledge of the materials and processes that exist in other star systems. Its fleeting presence is a reminder of the dynamic and often surprising nature of the cosmos.












Leave a Reply