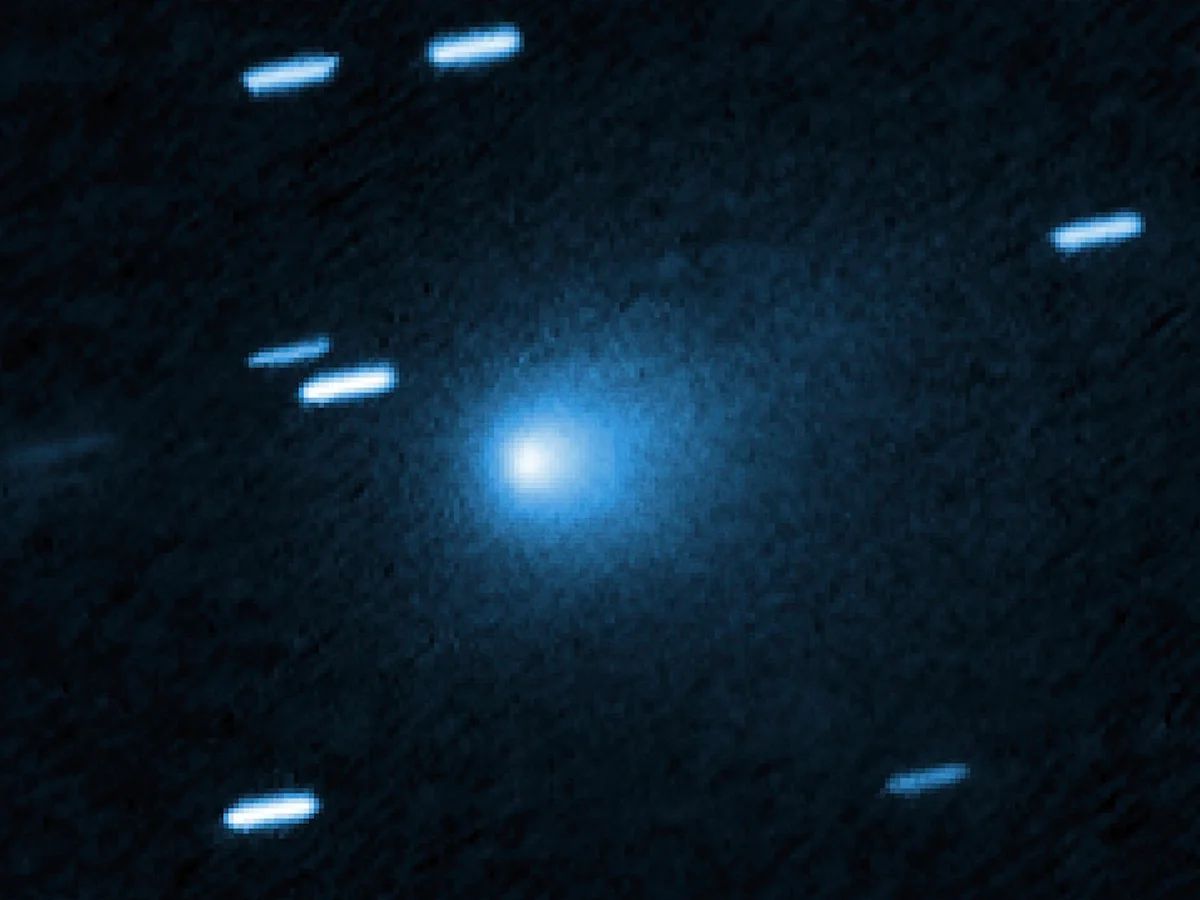
In a celestial event that has captivated astronomers and skywatchers alike, comet 3I/ATLAS is making its fleeting passage through our solar system. Discovered in July 2025 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-Impact Last Alert System (ATLAS), this interstellar comet is only the third confirmed object to enter our solar neighborhood from another star system, following the discovery of ‘Oumuamua in 2017 and comet Borisov in 2019. Its unique trajectory and composition offer scientists an unprecedented opportunity to study material that formed beyond our Sun’s influence, shedding light on the processes occurring in distant stellar environments.
Discovery and Trajectory
Comet 3I/ATLAS was first identified by the ATLAS survey, which specializes in detecting near-Earth objects and potential threats. The comet’s unusual hyperbolic orbit immediately indicated that it was not bound to the Sun and was instead passing through the solar system from interstellar space. Unlike comets originating from the Oort Cloud or Kuiper Belt, which circle the Sun on elliptical orbits, 3I/ATLAS is traveling at high velocity, on a path that will ultimately carry it back into the depths of the galaxy.
Its trajectory provides a unique observational window, allowing scientists to study an object that has been shaped by a stellar environment entirely separate from our own. By analyzing its motion and composition, astronomers hope to understand not only the physical and chemical properties of the comet but also the broader conditions present in other planetary systems.
Unprecedented Composition and Activity
Spectroscopic analysis of 3I/ATLAS has revealed a range of surprising features that distinguish it from solar system comets. Among these is a pronounced presence of cyanogen gas, a compound seldom seen in comets native to our Sun. Additionally, observations suggest a high carbon dioxide-to-water ratio, alongside a jet of nickel vapor without the typical accompanying iron, pointing to a chemical makeup that may reflect entirely different formation conditions in its home star system.
One of the most dramatic observations occurred on August 2, 2025, when a massive fan-shaped jet of gas and dust was captured erupting from the comet’s surface. Likely caused by sublimation from solar heating, this jet extends tens of thousands of kilometers into space and is oriented toward the Sun. Unlike the familiar solar wind-driven tail of a comet, this jet provides a direct glimpse into the internal composition and behavior of the nucleus, offering clues about how interstellar comets respond to the intense radiation and gravitational forces of a foreign solar system.
Scientific Significance
The passage of 3I/ATLAS offers an extraordinary scientific opportunity. Interstellar comets are natural probes of the wider galaxy, carrying chemical signatures and structural properties that have never been influenced by our Sun. Studying 3I/ATLAS allows researchers to compare the building blocks of distant star systems with those of our own, providing critical insights into planetary formation, volatile distribution, and the prevalence of organic compounds beyond the solar system.
Furthermore, observing its interactions with solar radiation and the solar wind allows scientists to test and refine models of cometary physics. Researchers are particularly interested in how the comet’s materials react to the intense heat and radiation during its closest approach to the Sun, which can reveal differences between interstellar and solar system cometary bodies.
Challenges in Observation
While the scientific community is eager to study 3I/ATLAS, its proximity to the Sun poses observational challenges. The comet is most visible during twilight, when the Sun’s glare complicates imaging from Earth-based telescopes. Despite these challenges, astronomers are employing a combination of ground-based observatories, space telescopes, and advanced spectroscopic instruments to capture detailed data. These efforts ensure that scientists can track its path, monitor its jet activity, and measure its chemical composition with unprecedented precision.
Public Fascination and Engagement
The rarity of interstellar comets has sparked public fascination. Astronomy enthusiasts around the world are keen to catch a glimpse of 3I/ATLAS through telescopes or binoculars during twilight. Outreach programs from observatories and space agencies are providing live streams and educational content, explaining the comet’s significance and offering guidance on observing it safely. Social media platforms are abuzz with images and updates, highlighting the unique experience of witnessing a visitor from another star system.
Implications for Understanding the Galaxy
Comet 3I/ATLAS is more than a scientific curiosity; it is a messenger from the galaxy, carrying information about the processes that shape planets and comets beyond our solar system. By analyzing its materials and behavior, astronomers can refine their understanding of how star systems form and evolve, the diversity of chemical compounds in space, and the potential for habitable environments elsewhere in the galaxy.
Its study also contributes to a broader understanding of cosmic interconnectivity. Every interstellar object passing through our solar system is a testament to the dynamic nature of our galaxy, reminding us that the Sun and its planets are part of a much larger, interconnected cosmic ecosystem.
Conclusion
The arrival of comet 3I/ATLAS is a rare and invaluable opportunity for both science and public engagement. As it traverses the solar system, astronomers are seizing the chance to study an interstellar object in unprecedented detail, exploring its composition, activity, and trajectory. Its journey offers a window into the distant reaches of the galaxy, providing clues about the formation of planetary systems, the prevalence of organic materials, and the fundamental processes shaping our universe.
For the public, 3I/ATLAS is a reminder of the vastness and dynamism of space—a fleeting celestial visitor that carries the secrets of another star system through our own, bridging the gap between the familiar and the truly alien.












Leave a Reply