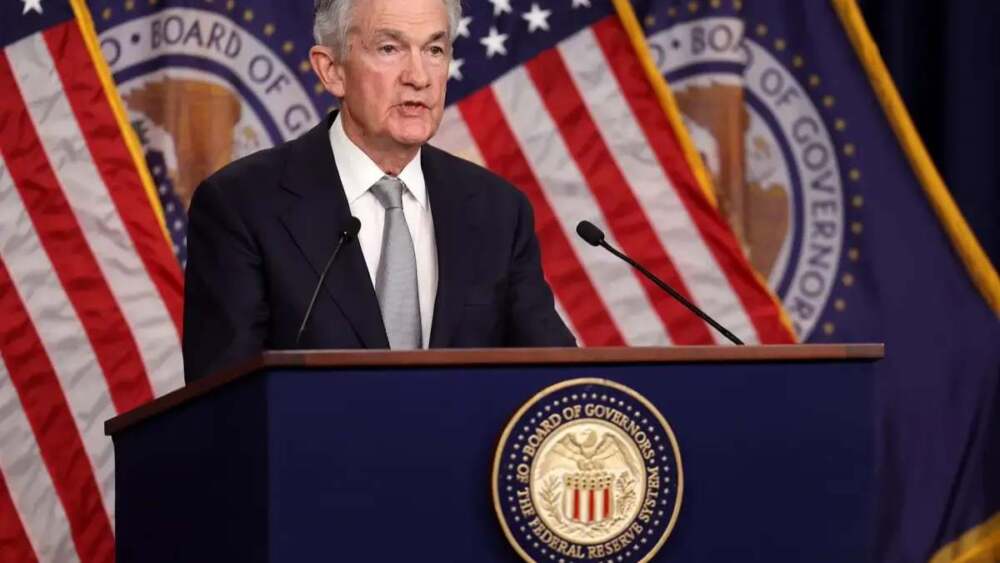
As of September 15, 2025, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell is navigating a complex economic environment marked by a cooling labor market and persistent inflation. The Federal Reserve is expected to implement a 25-basis-point interest rate cut this week, the first reduction in 2025. This decision reflects concerns about slow economic growth alongside rising prices—a combination of stagflationary pressures intensified by recent trade policies.
Despite the planned rate cut, dissent among Fed officials is anticipated. Some favor a larger reduction, while others advocate maintaining current rates, potentially resulting in a split decision—the first such divergence since 2019.
Inflation Pressures Remain High
In August 2025, U.S. consumer prices rose at an annual rate of 2.9%, marking the fourth consecutive month of accelerating inflation. Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, remained above 3%. Tariffs, particularly on automobiles, have contributed to higher production costs, further driving up consumer prices. These factors continue to create uncertainty around the effectiveness of the Fed’s rate adjustments.
Economic Outlook and Market Expectations
Economists suggest that while a quarter-point rate cut is likely in the upcoming meeting, the Fed may pause further reductions in October if inflation persists. Inflation pressures are particularly evident in sectors impacted by trade tariffs, signaling that price growth could continue in the near term.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve’s planned rate cut is intended to support economic growth and ease pressure on businesses and consumers. However, ongoing inflationary concerns and internal divisions within the Fed suggest that future monetary policy will remain cautious and heavily data-driven. Investors and policymakers alike are closely watching the central bank’s next moves, which will be pivotal in shaping the trajectory of the U.S. economy for the remainder of 2025.














Leave a Reply