Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have achieved a major breakthrough in the fight against antibiotic-resistant infections by using generative artificial intelligence (AI) to design new compounds capable of targeting superbugs. The team focused on two particularly dangerous bacteria: drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which causes gonorrhea, and multi-drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
AI-Powered Antibiotic Discovery
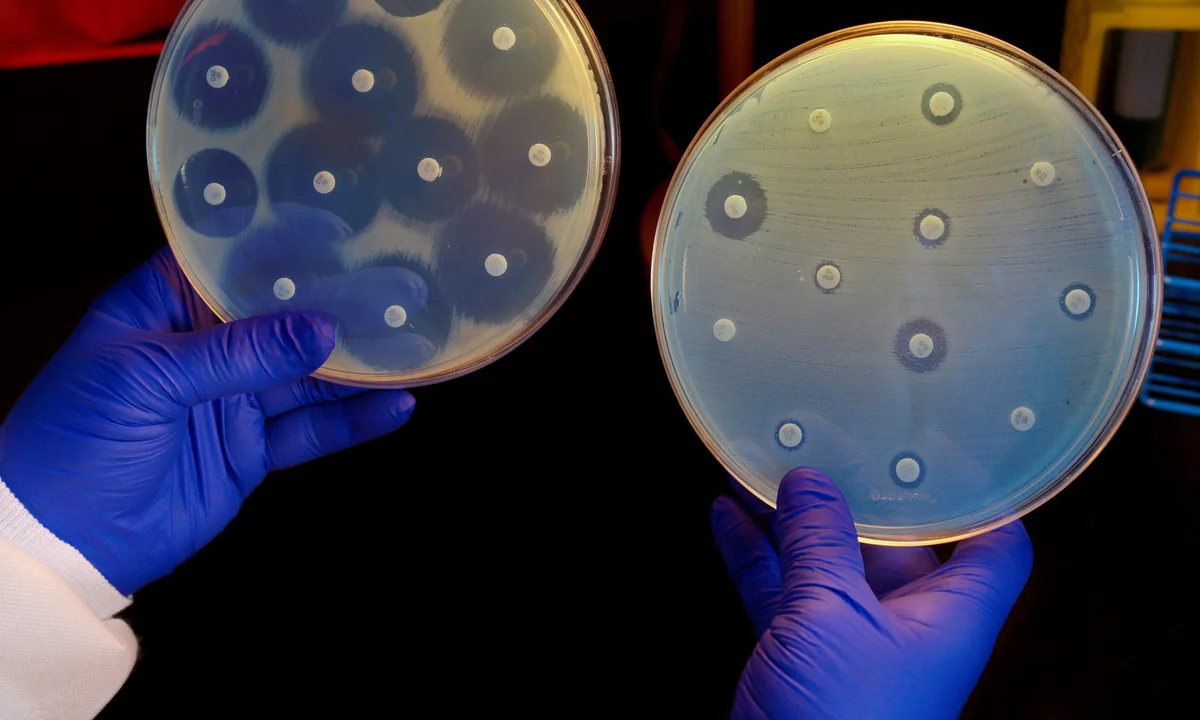
The scientists employed two AI-driven approaches to create potential antibiotic candidates. One method, called fragment-based design, built compounds from small molecular fragments, while the other, unconstrained design, allowed the AI to generate entirely new molecules atom by atom. From millions of generated structures, the team identified two promising compounds: NG1, effective against gonorrhea, and DN1, targeting MRSA. These molecules are structurally distinct from existing antibiotics, reducing the risk of cross-resistance.
Innovative Mechanisms
Both NG1 and DN1 work by disrupting bacterial cell membranes—a mechanism different from traditional antibiotics. NG1 specifically targets a protein involved in constructing the bacterial outer membrane, while DN1 interacts with multiple membrane components, making it harder for bacteria to develop resistance.
Promising Preclinical Results
In laboratory experiments, NG1 successfully eliminated drug-resistant gonorrhea in cell cultures and mouse models. DN1 also effectively treated MRSA infections in mice. These results suggest that AI-designed antibiotics could become a powerful tool in combating infections that no longer respond to conventional treatments.
Future Directions
The next steps involve refining NG1 and DN1 to improve their safety and effectiveness in humans, followed by clinical trials. Researchers also plan to use AI to develop treatments for other challenging pathogens, such as tuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Global Health Impact
This breakthrough highlights the potential of AI to accelerate antibiotic discovery at a time when antimicrobial resistance is a growing global health crisis. By rapidly designing and testing new compounds, AI can help overcome the slow and costly processes that have hindered traditional antibiotic development. The success of NG1 and DN1 demonstrates a promising new path in the fight against drug-resistant superbugs, offering hope for effective treatments in the near future.












Leave a Reply