NASA’s Artemis II mission, slated for April 2026, will mark the first crewed journey around the Moon since the Apollo era. This 10-day mission aims to test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, paving the way for future lunar landings. However, beyond its technological objectives, Artemis II will also serve as a comprehensive human health study, with astronauts acting as both researchers and subjects.
Dual Role of Astronauts
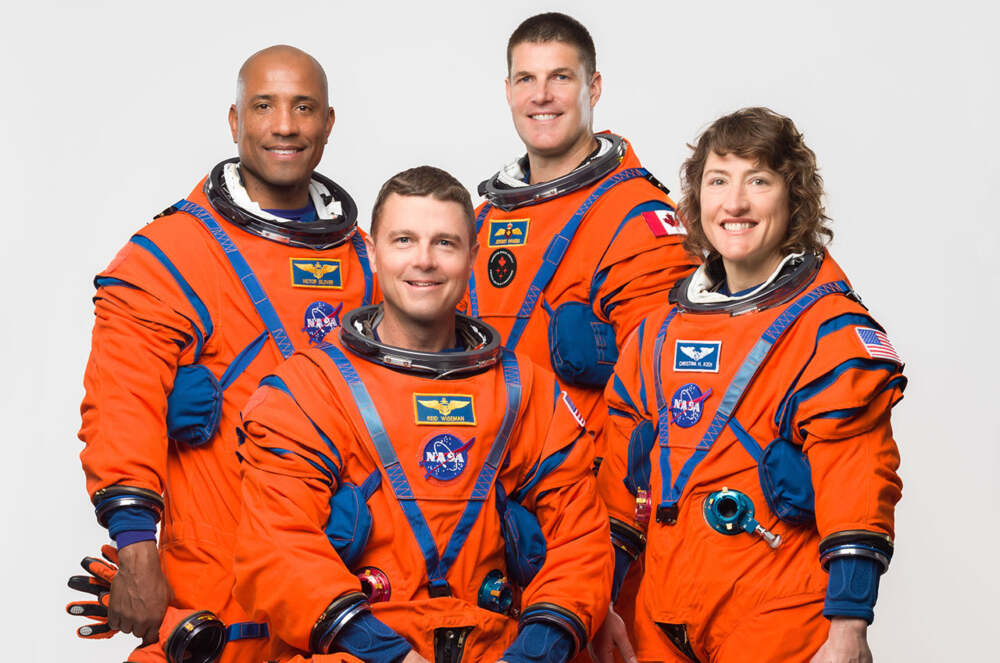
The Artemis II crew—NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Canadian Space Agency astronaut Jeremy Hansen—will participate in a series of health studies to understand how deep space travel affects the human body. These studies will focus on various aspects of human health, including:
- Sleep Patterns: Monitoring changes in sleep quality and duration due to microgravity and altered light cycles.
- Stress Levels: Assessing psychological stressors and their impact on crew performance and well-being.
- Immune System Function: Evaluating how spaceflight influences immune responses and susceptibility to infections.
- Radiation Exposure: Measuring the effects of cosmic radiation on the body during deep space missions.
To collect data, astronauts will provide biological samples such as blood, saliva, and urine. They will also wear wrist monitors to track movement and sleep patterns. This data will be invaluable for NASA’s Human Research Program, aiding in the development of countermeasures to ensure astronaut health on future missions.
Innovative Research Tools
In addition to traditional health monitoring, Artemis II will utilize advanced research tools to study the effects of spaceflight on human health:
- Organ-on-a-Chip Devices: These miniature models of human organs will be used to study cellular responses to microgravity and radiation.
- Radiation Dosimeters: Small devices that will measure the levels of radiation astronauts are exposed to during the mission.
These tools will provide real-time data on how spaceflight conditions affect human biology, offering insights that are not possible through Earth-based studies.
Importance for Future Exploration
The data collected during Artemis II will be crucial for planning long-duration missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Understanding how spaceflight impacts human health will allow NASA to develop effective countermeasures to mitigate risks associated with radiation, muscle atrophy, bone density loss, and psychological stress. This research is essential for ensuring the safety and success of future deep space missions.
Conclusion
NASA’s Artemis II mission represents a significant step forward in human space exploration. By studying the effects of deep space travel on human health, the mission will provide valuable data to support the development of technologies and strategies to protect astronauts on future missions. As humanity looks toward returning to the Moon and venturing to Mars, the insights gained from Artemis II will be instrumental in ensuring the health and safety of astronauts on these ambitious journeys.












Leave a Reply