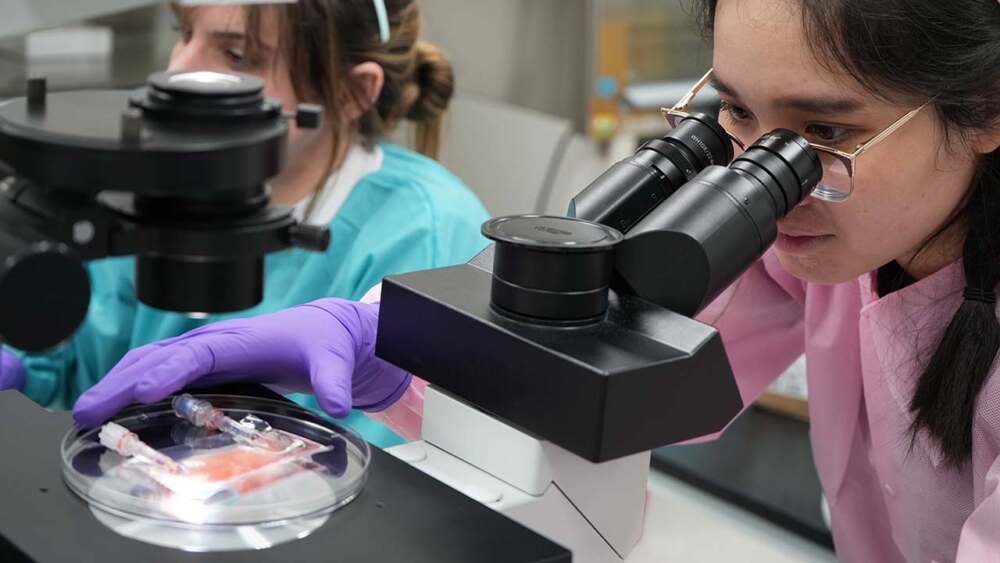
September 2025 — A new scientific study has raised concerns about the long-term health effects of space travel. Researchers have discovered that human blood-forming stem cells, vital for maintaining the immune system and producing blood, may age up to ten times faster in space than on Earth.
What Scientists Observed
Scientists monitored hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells aboard the International Space Station for several weeks. Compared to cells kept under identical conditions on Earth, those exposed to microgravity and cosmic radiation showed:
- Reduced ability to renew themselves
- Increased DNA damage and telomere shortening
- Signs of cellular stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
- Greater risk of mutations linked to blood cancers
The changes appeared in just over a month — a pace equivalent to decades of aging in normal Earth conditions.
Hope for Reversal
While the findings are alarming, researchers noted a glimmer of hope: when the damaged cells were later returned to healthy environments, some of the aging effects began to reverse. This suggests that medical interventions could one day help astronauts recover or protect themselves during long missions.
Why It Matters
- Astronaut Health: Rapidly aging stem cells could weaken astronauts’ immunity, making them more vulnerable to infections, anemia, and even cancer. This risk becomes especially pressing for future missions to Mars or other deep-space destinations.
- Understanding Aging: Because aging processes appear to accelerate in space, scientists can use it as a model to study how age-related diseases develop — and potentially find treatments more quickly.
- Earth Benefits: The insights could also help researchers on Earth combat conditions like immune decline, blood disorders, and age-related diseases.
Looking Ahead
Researchers are now planning more in-depth studies, including monitoring astronauts’ cells directly during missions. They are also exploring potential countermeasures, such as drugs or genetic therapies, to preserve stem cell health in space.












Leave a Reply