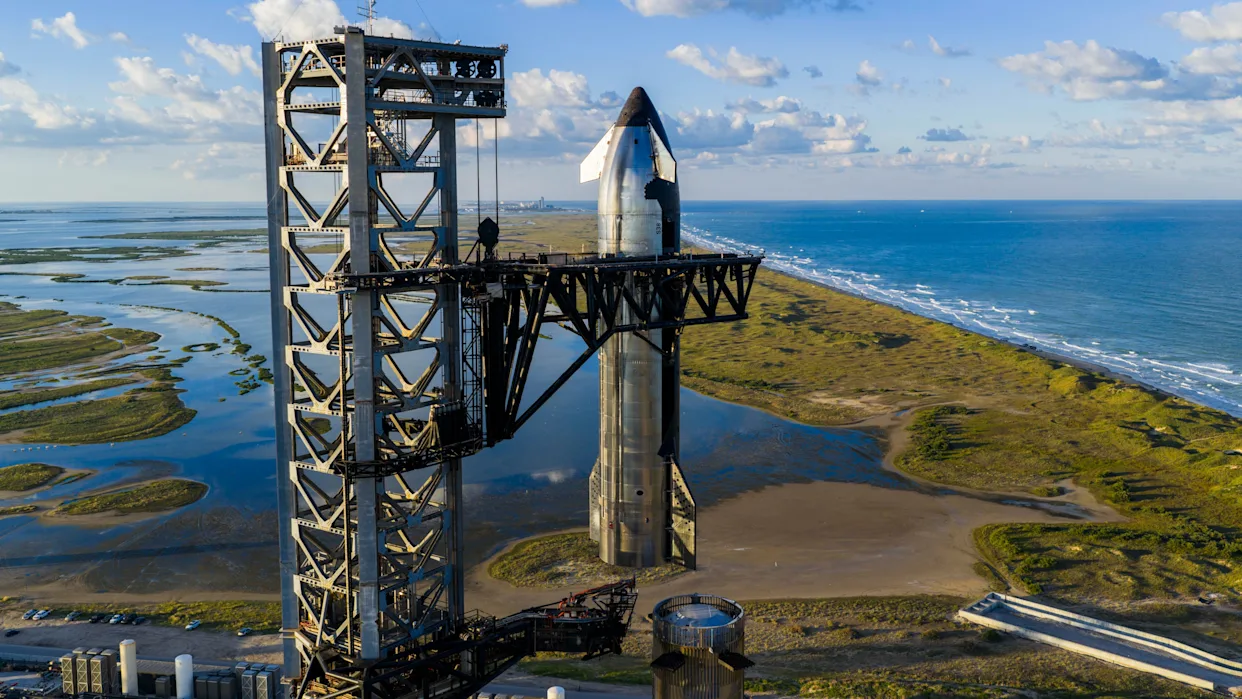
The countdown has begun for one of the most highly anticipated space missions of the year. SpaceX is preparing for the eleventh integrated test flight of its revolutionary Starship and Super Heavy rocket system — a flight that could redefine the boundaries of reusable spacecraft technology. Scheduled to lift off from the company’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, the mission represents not only another technical trial but also the symbolic end of an early chapter in SpaceX’s grand vision for interplanetary travel.
A Launch with Global Attention
According to SpaceX, the target launch window for Starship Flight 11 opens on Monday, October 13, at 7:15 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time (6:15 p.m. Central Time). The window will remain open for roughly 75 minutes, giving the company flexibility in case of last-minute adjustments or weather concerns.
This launch is expected to draw millions of online viewers, along with hundreds of onlookers near the Texas Gulf Coast. Space enthusiasts, industry experts, and NASA officials alike are closely following the event — not only for the technological spectacle but also for what it represents in the future of spaceflight.
The Final Flight of the Current Starship Design
Flight 11 is being hailed as a turning point in the Starship development program. It will be the final mission for the current “Version 2” design of both Starship and its powerful Super Heavy booster. Future missions will feature a major hardware overhaul — from reengineered Raptor engines to updated structural configurations aimed at achieving full reusability.
SpaceX’s founder and CEO, Elon Musk, has repeatedly stated that each Starship flight is as much about data gathering as it is about performance. “We’re iterating faster than any rocket program in history,” he said in a previous briefing. “Each flight gives us thousands of new data points that guide the design of the next generation.”
That philosophy has defined the Starship testing campaign: fail fast, learn faster, and build smarter. Flight 11 embodies that spirit — an ambitious attempt to push the boundaries of flight stability, heat shielding, and booster recovery.
What Flight 11 Aims to Achieve
While earlier flights demonstrated successful stage separation and partial reentry control, Flight 11 aims to combine these milestones into a single, fully realized test. SpaceX engineers have outlined several key objectives:
- Refined Stage Separation and Engine Burn Sequences
Starship’s two-stage design involves a “hot staging” technique, where the upper stage ignites while still attached to the booster. This approach saves fuel and simplifies design but generates enormous stress. Engineers hope to refine this timing further for smoother separation. - Booster Recovery Test Using a New Landing Burn Profile
The Super Heavy booster will attempt an ocean landing using a new five-engine to three-engine landing sequence, a crucial step toward future full-pad recoveries. - Orbital Maneuvering and Reentry Validation
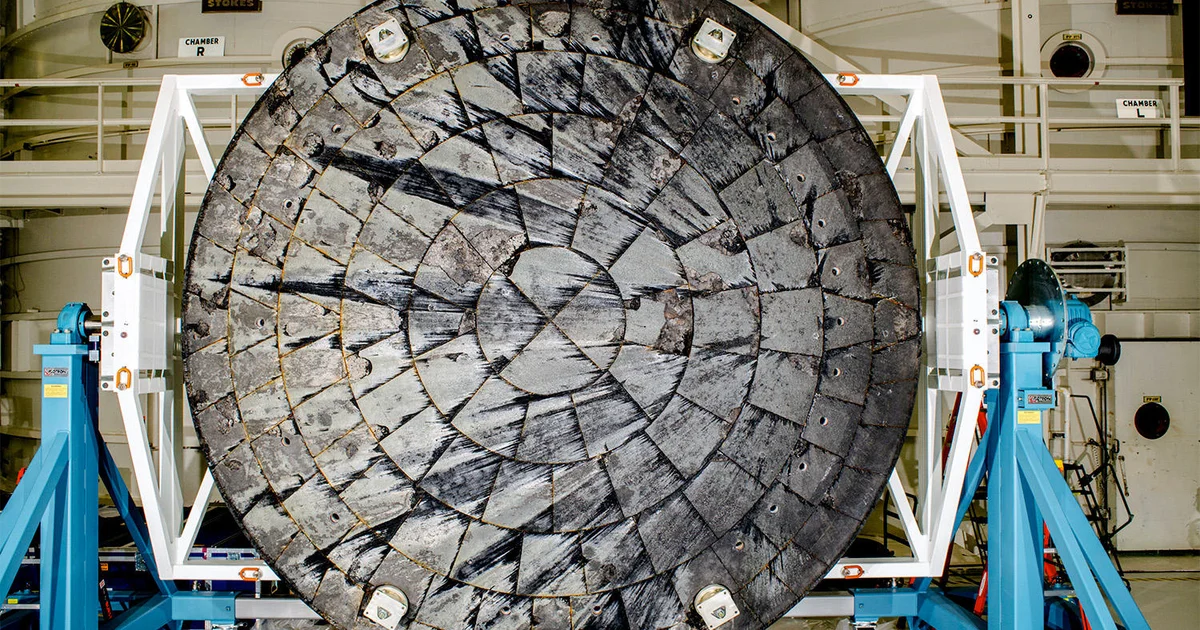
The Starship upper stage is expected to complete a near-orbital flight path before reentering Earth’s atmosphere over the Indian Ocean. The test will validate improvements to the heat shield, made of thousands of hexagonal ceramic tiles. - Controlled Splashdown and Data Retrieval
The mission’s end goal is to achieve a controlled splashdown while transmitting real-time telemetry. Data collected will inform redesigns for the next-generation vehicles expected to debut in 2026.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the successes of prior tests, Starship remains the most complex rocket ever built — and that complexity comes with risks.
Each of the 33 Raptor engines on the Super Heavy booster must ignite and throttle flawlessly during liftoff. Even minor engine anomalies can cause catastrophic outcomes. Likewise, reentry exposes the Starship’s heat shield to temperatures exceeding 1,500°C, testing the durability of its thermal protection system.
Another major challenge is precision recovery. SpaceX’s long-term goal is to catch the returning booster using the massive “Mechazilla” launch tower arms — an audacious move that has never been attempted. While Flight 11 won’t perform a catch attempt, it will gather data crucial for those future landings.
A Transition to Starship’s Next Era
Following Flight 11, SpaceX plans to pause Starship launches temporarily to implement a major series of upgrades. This will include improvements to propellant management systems, avionics, and engine clusters. The new version — informally referred to by engineers as “Starship V3” — will be built for rapid reusability, allowing turnaround times measured in days rather than weeks or months.
These upgrades are not just about performance; they’re essential for meeting NASA’s Artemis program timelines. Starship has been selected as the lunar lander for the Artemis III mission, which aims to return humans to the Moon later this decade. NASA’s schedule depends on SpaceX’s ability to demonstrate reliable, repeatable Starship launches and landings.
Economic and Strategic Significance
Beyond the technical milestones, Flight 11 carries significant economic implications. Starship’s success could dramatically reduce the cost of launching satellites and deep-space missions. SpaceX’s long-term vision is to enable point-to-point travel on Earth using Starship, as well as crew and cargo missions to Mars.
A fully reusable Starship could lower launch costs to under $10 million per flight — a fraction of current orbital missions. That economic model would disrupt both the government and commercial launch sectors, forcing competitors and international agencies to rethink their own development programs.
Public Excitement and Global Impact
As with every major SpaceX launch, public anticipation is running high. Hotels around Brownsville and South Padre Island are nearly fully booked, with spectators hoping to witness the world’s most powerful rocket rise into the sky once more.
Online, space enthusiasts and amateur engineers have flooded social media with renderings, simulations, and discussions. Educational institutions across the world plan to stream the event live for students, emphasizing the mission’s value as a learning opportunity in aerospace engineering and innovation.
Looking Toward the Future
Whatever the outcome of Flight 11, it will mark a defining milestone for SpaceX and for humanity’s path toward becoming a multi-planetary species.
If successful, it will demonstrate that fully reusable super-heavy lift systems are not only possible but practical — paving the way for affordable access to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Even in the case of failure, the lessons learned will accelerate development and bring the next generation of Starship vehicles closer to operational readiness.
Elon Musk has repeatedly described Starship as “a machine to make other worlds possible.” With Flight 11, that dream inches closer to reality.












Leave a Reply