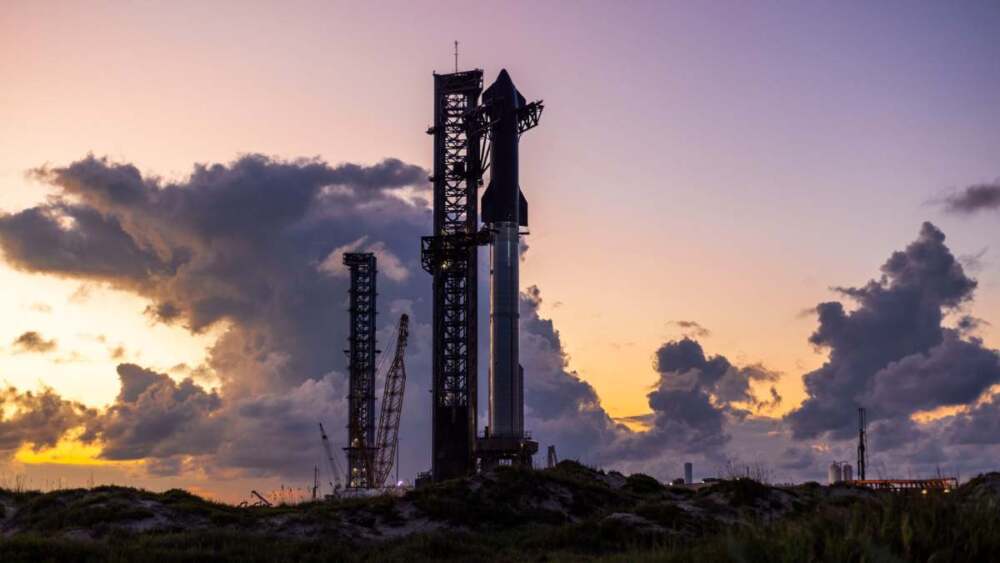
SpaceX has once again made history with the successful completion of the 11th test flight of its colossal Starship rocket, the most powerful spacecraft ever built. The mission, conducted from the company’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, marked another bold stride toward SpaceX’s long-term goals of lunar exploration, Mars colonization, and fully reusable spaceflight.
This latest test was not merely another demonstration of capability — it represented a decisive turning point in the development of the next-generation spacecraft designed to transport humans and cargo far beyond Earth’s orbit. With each test flight, SpaceX inches closer to revolutionizing space travel, and Flight 11 has provided the most complete and successful performance of Starship’s systems to date.
A Flawless Launch and Controlled Flight
The launch occurred under clear skies, with Starship’s Super Heavy booster roaring to life and propelling the 400-foot-tall rocket into the heavens. The sheer power of its Raptor engines, fueled by liquid methane and oxygen, once again showcased SpaceX’s engineering prowess. After liftoff, the Super Heavy completed a smooth ascent and executed a clean stage separation, allowing the Starship upper stage to continue into space.
During its ascent, the spacecraft achieved several critical milestones, including engine re-ignition sequences, aerodynamic control tests, and a modified heat shield configuration designed to evaluate material durability during high-velocity reentry. Engineers monitored real-time data as the vehicle climbed toward its target altitude before beginning its descent back toward Earth.
The booster, meanwhile, performed an advanced controlled descent and splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico. Though not a full recovery, the landing maneuver was near-perfect — an impressive achievement for a rocket of such scale. The data gathered from this controlled splashdown will help SpaceX refine future booster reuse strategies, a core component of the company’s cost-efficiency model.
The Starship Upper Stage: Pushing Boundaries
Once separated from the booster, the Starship upper stage continued its suborbital trajectory, testing its stability and propulsion systems in near-space conditions. The spacecraft carried simulated payloads to replicate satellite deployment scenarios, mimicking real-world operations for Starlink or lunar cargo missions.
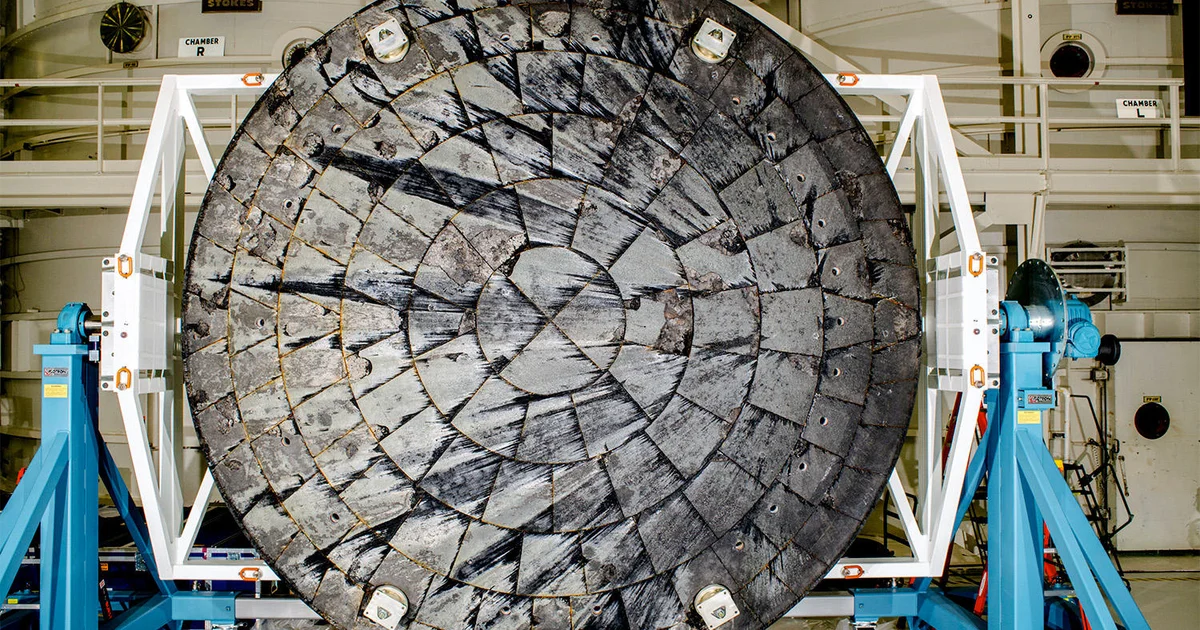
A particularly critical aspect of this test was the evaluation of Starship’s heat shield, which endured intense reentry conditions. Engineers intentionally exposed sections of the thermal tiles to extreme stress to measure their heat resistance and flexibility. These tests are vital to ensuring that Starship can safely return through Earth’s atmosphere — and, in the future, the thin, volatile atmosphere of Mars.
After approximately one hour of flight time, the upper stage splashed down in the Indian Ocean, completing a near-flawless test sequence. Every phase — from ascent to reentry — yielded valuable data that will inform the design of Starship’s next-generation variants.
From Testing to Transformation
SpaceX confirmed that this 11th flight marks the final phase of its current prototype series. The company will now transition to new Starship iterations designed with improved engines, stronger heat protection, and faster turnaround capabilities.
Future versions will be directly tied to NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon within the next few years. Starship’s role as a lunar lander — delivering astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface — makes it a central element in the future of U.S. space exploration. Additionally, orbital refueling demonstrations, one of the most ambitious upcoming milestones, will prove critical for extending Starship’s range to Mars.
SpaceX has already begun work on integrating automated docking systems, expanded payload capacity, and in-space cryogenic fuel transfer — technologies that will enable true interplanetary missions.
Engineering the Future of Reusability
Reusability has always been at the core of SpaceX’s philosophy. The success of Falcon 9 landings revolutionized the commercial launch industry, and now, Starship seeks to push that frontier even further. By reusing both the booster and the spacecraft multiple times, SpaceX aims to reduce the cost of access to orbit by more than 90%, potentially unlocking a new era of affordable deep-space missions.
However, challenges remain. The heat shield integrity, engine performance during multiple reuses, and regulatory hurdles for frequent launches still need to be addressed. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) continues to work closely with SpaceX to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards, especially as the company aims to conduct more rapid launch cadences from Starbase.
A Leap Toward Mars
Beyond the technical triumphs, this flight symbolizes SpaceX’s enduring mission — to make humanity a multiplanetary species. Elon Musk has often described Starship as “the vehicle that will carry civilization to other worlds.” With this successful test, that once-distant dream feels more tangible than ever.
The company’s roadmap includes establishing fuel depots in orbit, developing Martian habitats, and transporting scientific and industrial payloads across planets. The advances achieved in Flight 11 — from engine reliability to aerodynamic control — represent vital steps toward these ambitious goals.
Industry Impact and Global Excitement
The space industry has taken notice. Competitors and collaborators alike have praised SpaceX’s progress. NASA officials called the test “a monumental step forward,” while private aerospace experts highlighted how Starship’s design could redefine space logistics and planetary science missions for decades to come.
Online, enthusiasm exploded across social media platforms, with thousands of users celebrating what many described as “a new dawn in space exploration.” The global interest in Starship’s evolution reflects the broader excitement surrounding the new space race, where private innovation leads the charge toward the stars.
Conclusion
With its 11th Starship flight, SpaceX has demonstrated a level of operational sophistication and technological maturity unmatched in modern aerospace. Each test brings humanity closer to the next great leap — not just to the Moon, but to Mars and beyond.
While obstacles remain, the vision that drives SpaceX is clearer than ever: a future where space travel is sustainable, routine, and open to all of humanity. As the world watches the Starship program evolve, it’s evident that this flight was not just another test — it was a historic moment that propels us toward the next frontier.












Leave a Reply